Maker of the Optical Design Software OpTaliX
Light Pipe, Step Index Fiber
In light pipes and step index fibers, rays enter a tube (being either solid or hollow) and reflect from the walls in an indeterminate number of times until they emerge. The end surfaces may have any form (spherical, aspherical, Fresnel, etc.) and may also be arbitrarily tilted.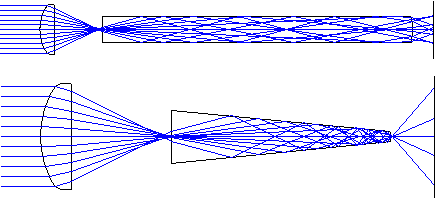
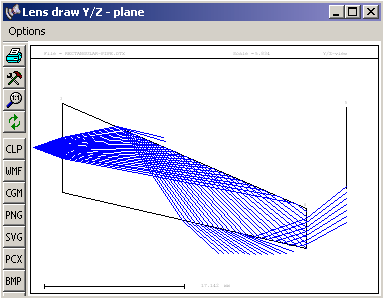
Light pipes are formed by extruded surfaces and are handled by the sequential surface model. Circular or rectangular cross sections are supported. All forms may be tapered. Rectangular light pipes can also be sheared (see figure below). Violation of total internal reflection (TIR) in solid pipes is taken into account.
Overview
Examples
- Non-Sequential
- Special Apertures
- Gradient Index
- Hologram
- Zoom
- Array Surfaces
- Fresnel Lens
- Light Pipe
- Global References
- Geometric Analysis
- Diffraction Analysis
- Interferogram
- Physical Optics (350kb)
- Fibers
- Optimization
- User Defined Graphics
- Glass Manager
- Coatings
- Macro Language
- ISO Element Drawing
- Surface Deformations
- Ghost Image Analysis
- Illumination