Maker of the Optical Design Software OpTaliX
Holographic/Diffractive Surfaces
The optical properties of a holographic surface are based on diffraction at the effective grating spacing seen at the local intersection point of a ray. Commonly, holographic surfaces are also denoted as diffractive surfaces. To model these effects, several types of diffractive surfaces are available in OpTaliX.- Linear grating
- Optical hologram, formed by interfering two beams of light,
- Computer-generated holograms (CGH) with a user specified radial symmetric phase distribution,
- Computer-generated holograms (CGH) with a user specified asymmetric (two-dimensional) phase distribution,
- ''Sweatt'' model.
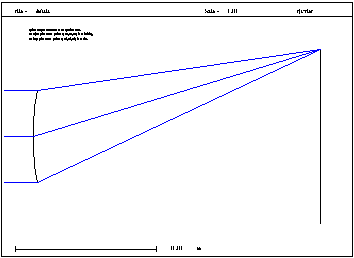 |
Two-Point Hologram: This type of holographic surface describes the interference pattern of two point sources, i.e. two spherical waves, which includes plane wavefronts as the limiting case. |
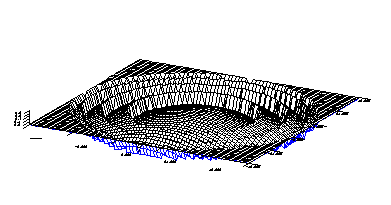 |
Phase Map. The phase distribution can be shown for all user specified symmetric and asymmetric phase functions including the 2p phase steps. |
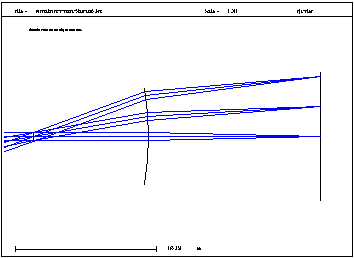 |
Sweatt Model. A diffractive lens is mathematically equivalent to a thin refractive lens, provided the index of refraction goes to infinity. For practical cases a very high refractive index (n = 10000) is used. This model is commonly known as the "Sweatt" model. Shown to the left is a F-q scan lens, which illustrates the use of the sweatt model for a diffractive lens. |
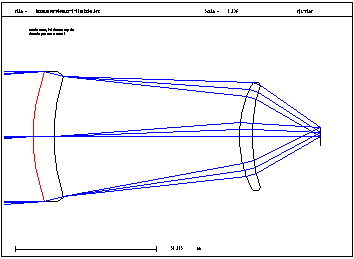 |
Diffractive Germanium Doublet. A color corrected F/1.0 system for the 8-12mm wavelength range. The first surface is aspheric while the second surface bears a CGH, described by a symmetric phase function. |
Overview
Examples
- Non-Sequential
- Special Apertures
- Gradient Index
- Hologram
- Zoom
- Array Surfaces
- Fresnel Lens
- Light Pipe
- Global References
- Geometric Analysis
- Diffraction Analysis
- Interferogram
- Physical Optics (350kb)
- Fibers
- Optimization
- User Defined Graphics
- Glass Manager
- Coatings
- Macro Language
- ISO Element Drawing
- Surface Deformations
- Ghost Image Analysis
- Illumination